The number Pi (π) is the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. Pi has a wide range of applications such as geometry, trigonometry, engineering, art. In this article, you’ll learn how to use PI function in Excel and PI approximations with examples.
Excel PI Function and Usage
Excel PI function returns the mathematical constant pi value that is approximately equal to 3.14159. Excel returns it accurate to 15 digits. It can be shown as a ratio 22/7, which is commonly used to approximate it in math.
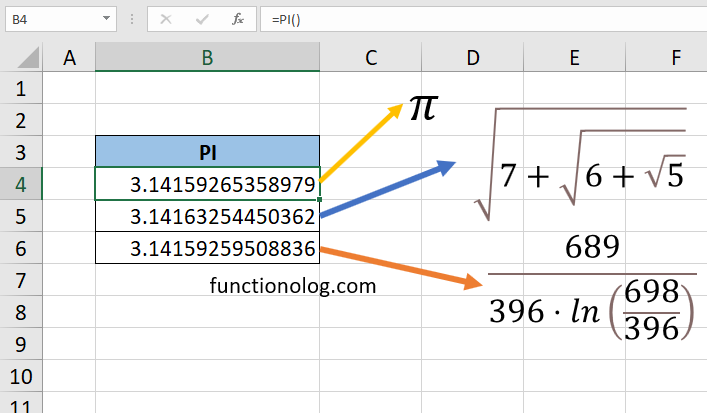
Given that the PI function it doesn’t require any arguments in Excel, you can simply call it in a cell. Here’s the steps on how to get the number of pi in Excel:
- Pick the cell where you’d like the pi number to show up
- Type the formula =PI() to the cell.
- Enter to get the number.
PI number and approximation formulas in Excel
Pi (π) is an irrational number. Its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. However, approximations of the number of pi are often used for practical calculations. Some common approximations of pi you can use in Excel:
- 3.14: This is a commonly used approximation. It’s easy to remember and a reasonable accuracy for some calculations.
- 22/7: Another well-known approximation is 22/7 which is a fraction that is close to pi.
- 355/113: This fraction is a more accurate than 22/7. It is used for calculations in which higher precision is needed.
- Euler’s method: 20*arctan 1/7 + 8*arctan 3/79
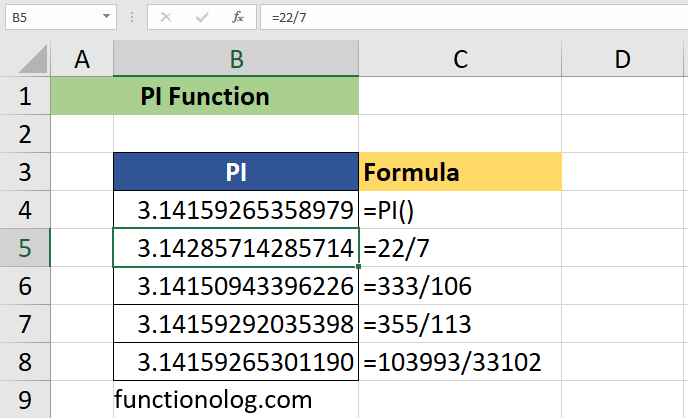
Instead of using the PI() function, you may want to use approximations of number of pi in Excel. For instance, 355/113 approximates π to 6 decimal place. 103993/33102 gives 9 correct digits.
PI number for Engineering Calculations
Here are some examples of how the mathematical constant π (pi) is used in various calculations:
- Geometry: PI (π) is a fundamental constant in geometry. It is used to calculate the circumference (C) and area (A) of a circle.
- Physics: PI appears in various physics equations, including waveforms, oscillations.
- Trigonometry: The unit circle is used to describe the values of trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan, etc.) at different angles, and π plays a key role in these calculations.
Suppose you want to calculate the sine and cosine of an angle in radians using Excel. For example, to calculate COS(30°), you need to express the degree 30 in radians. That means you should convert it. We know that Degree = Radian measure × (180°/π). From this, we get π/6 for the degree 30.
The PI number is used in circumference and area calculations. Circumference (C) is calculated with 2πr, where r is the radius of the circle. Area is calculated with πr², where r is the radius of the circle. In Excel, type directly =2*PI()*r and =PI()*r^2 respectively.