GCD and LCM help to simplify calculations, and solve problems involving “Fractions”, “Time and Distance Problems”, “Solving Equations” and in various contexts. In this article, you will learn how to calculate greatest common divisor and least common multiple by using GCD and LCM function in Excel.
GCD function and how to use it in Excel
The greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is a mathematical concept used to describe the largest positive integer that divides two or more numbers without leaving a remainder.
Excel GCD function returns the greatest common divisor of two or more numbers. The greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides them. For example, consider the numbers 12 and 18. The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, while the factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The largest number that appears in both lists of factors is 6, so the GCF (or GCD) of 12 and 18 is 6.
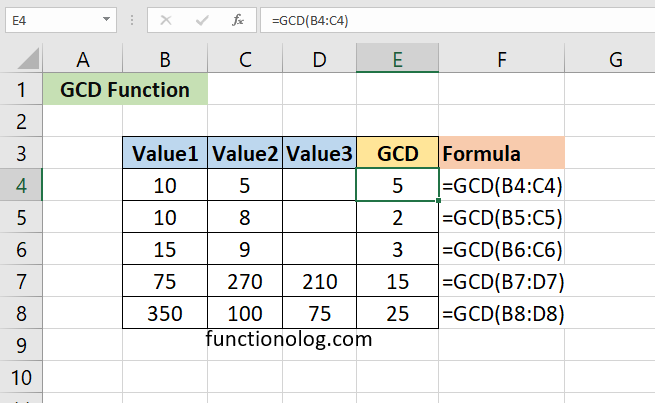
The formula =GCD (15,9) gives the greatest common divisor of 15 and 9. The result is 3, since 3 divides both 15 and 9.
Real-world problems using GCD function
To better understand the greatest common divisor and the usage of Excel GCD function, let’s see some real-world examples.
- GCD problem 1: A Coach has 18 female players and 12 male players. How many teams with equal numbers of females and males can be made?
The players needs to be divided into smaller groups. To find the GCF of the numbers of the players, use the formula =GCD (18,12). The GCD is 6 so that six teams made up of 2 males and 3 females.
- GCD problem 2: You’ve freshly baked 15 cheesecake and 24 Vanilla Cake for packaging. Your aim is to distribute the cakes into an equal amount of containers, ensuring an equal amount of each cake type per container. how many containers you’ll need to pack as many cakes as possible?
15 -> 1, 2, 3, 5, 15, …
24 -> 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24, …
This problem can be solved with the formula =GCD (15,24). So, we find 3 containers for the cakes.
LCM function and the usage in Excel
The least common multiple (LCM) describes the smallest positive integer divisible by two or more given numbers. In other words, it is the smallest common multiple that all the numbers share. For example, consider the numbers 4 and 6. The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, … and the multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36. The smallest number that appears in both lists of multiples is 12, so the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
Excel LCM function returns the least common multiple of two or more numbers. The least common multiple of numbers is the smallest number that is evenly divisible by given numbers.
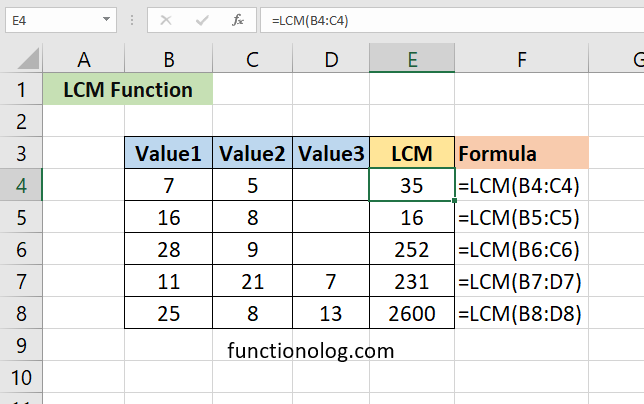
The following formula gives the least common multiple of 16 and 8. 16, 32, 48, … are common multiples of 16 and 8. The number 16 is the smallest. Therefore, 16 is called the least common multiple.
=LCM (16,8)
GCD and LCM function are available in Excel 2003 and later versions.
Real-world examples with LCM function
To better understand the least common multiple and the usage of the LCM function, let’s see some real-world examples and solve them using Excel.
- LCM Problem 1: Packaged fruits are available in quantities of 5 apples and 8 pears each. Our goal is to buy the smallest number of packages containing both apples and pears, ensuring that exactly 1 apple per pear. What is the minimum number of packages required for this?
For this problem, the least common multiple is calculated with the formula =LCM(5,8). The result is 40. We find 40/5 = 8 packages of apples and 40/8 = 5 packages of pears.
- LCM Problem 2: Two lights are simultaneously activated. One flashes every 2 seconds, while the other flashes every 3 seconds. Over a span of 15 seconds, how many times will they flash together?”
2 -> 2, 4, 6, 8, 10
3 -> 3, 6, 9, 12
With the formula =LCM (2,3), The least common multiple of 2 and 3 is 6. In 15 seconds, 30/6 = 5 times they flashes at the same time.
GCD and LCM Tips & Tricks
You need to know some tips and tricks to avoid mistakes when using GCD and LCM function:
- The GCD and LCM function allows you to input a maximum of 255 numbers.
- The GCD and LCM function runs with whole numbers. Using non-integer values could lead to inaccurate outcomes.
- They require a minimum of two numbers to calculate the greatest common factor and the least common multiple.